World Diabetes Day 2023: Diabetes – A Growing Health Concern
In recent times, the prevalence of diabetes has become alarmingly common and requires our attention. It is no longer an uncommon disease that we casually hear about. Have you ever wondered why Diabetes has turned into a lifestyle disorder? Is it possible to prevent or delay its onset? And what are the available diagnosis options?
On World Diabetes Day 2023, in line with this year’s theme “Empowering Global Health,” our blog is dedicated to addressing your concerns by offering the timely diagnosis options. Join us as we delve deeper into this condition and enhance your understanding.
Understanding Diabetes
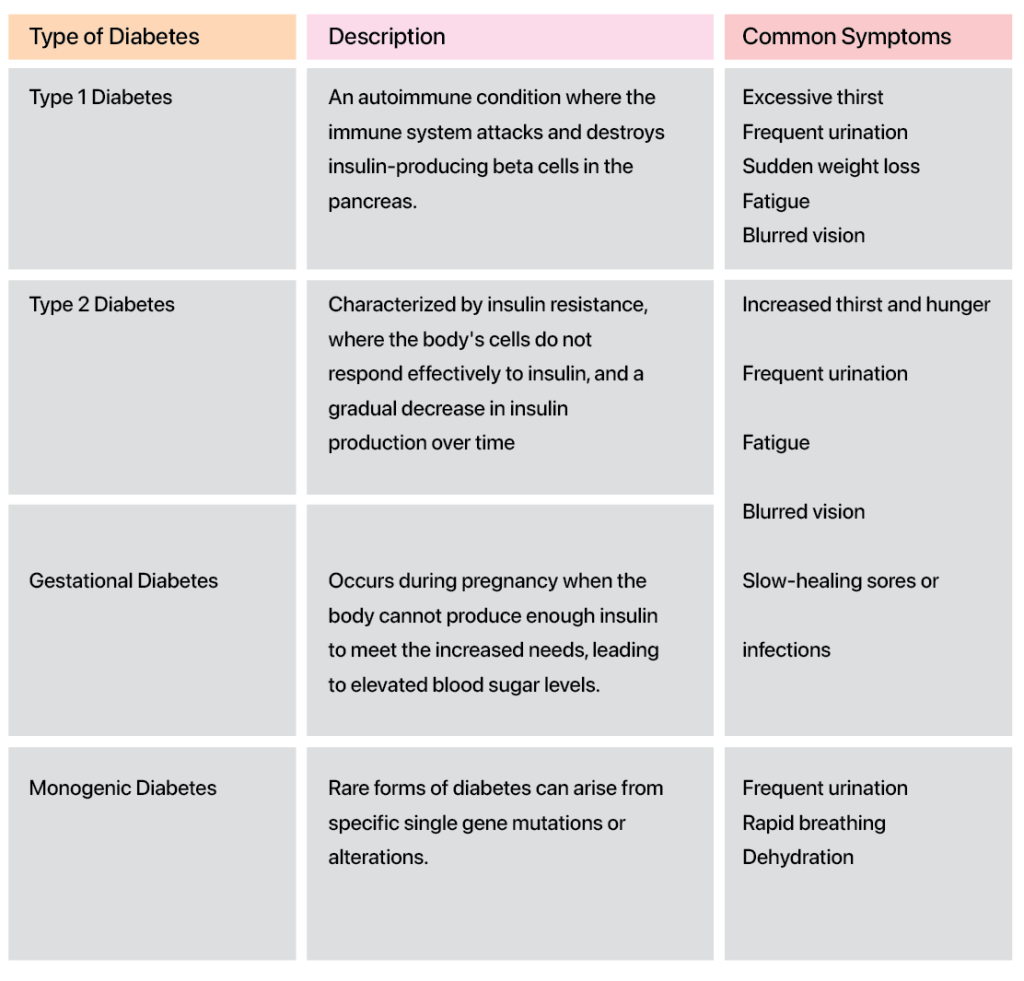
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the body’s ability to convert food into energy. When we eat, our body breaks down most of the food into sugar (glucose) and releases it into the bloodstream. To regulate blood sugar levels, the pancreas releases insulin, which acts like a key to allow sugar into the body’s cells for energy.
However, in the case of diabetes, either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or it cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, as excess sugar remains in the bloodstream. Over time, this can result in serious health complications, including heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease.
Prevalance of Diabetes in India and Abroad
Globally, diabetes is a growing health concern, with a steady rise. In 2017, 8.8% of adults were affected, and projections for 2045 predict a worrisome increase to 9.9%, translating to a surge from 424.9 million in 2017 to 628.6 million in 2045.
India ranks as the world’s second-largest country for diabetes, hosting 62 million affected individuals, a number projected to surpass 100 million by 2030, according to the International Diabetes Federation Atlas. Over 95% of cases in India are attributed to Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
Unfortunately, MODY cases often face misdiagnosis as Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, leading to inappropriate insulin treatments.
What does Yoda Diagnostics offer?
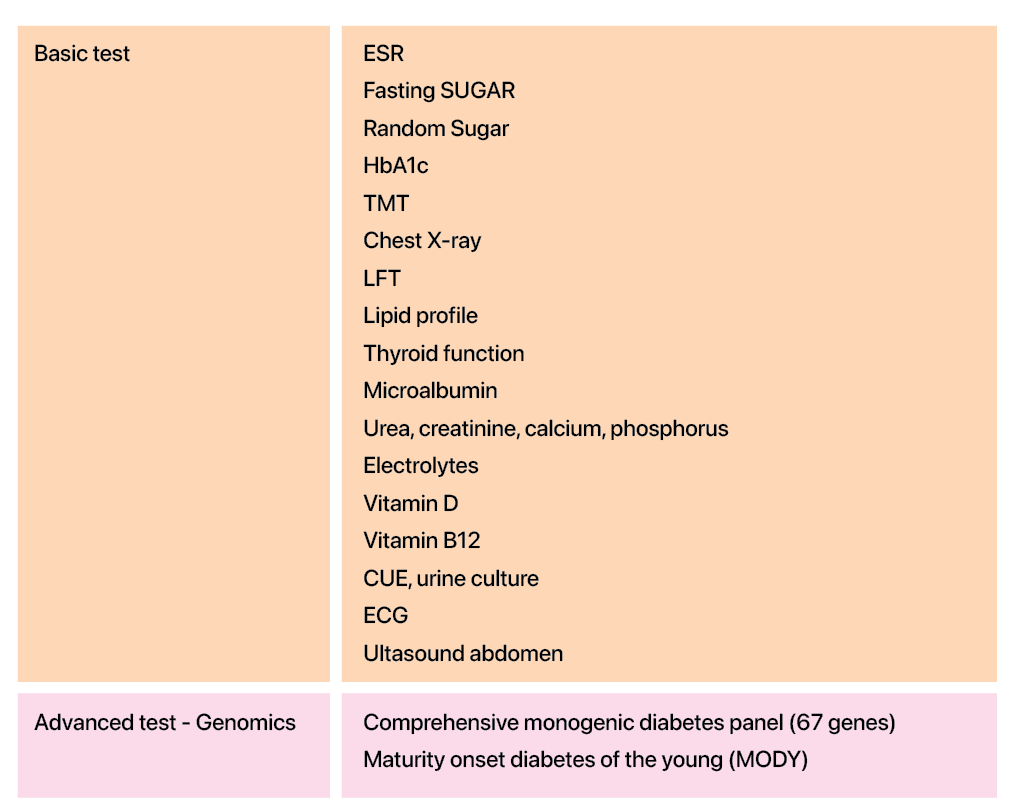
In order to avoid misdiagnosis, Yoda Diagnostics offers an extensive range of tests under the Diabetes Panel.
What are the benefits of keeping HbA1c levels in reasonable limits?
In order to diagnose diabetes, the American Diabetes Association has recommended glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) as a substitute to fasting blood glucose.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a valuable blood test that provides information about a person’s average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. The test measures the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that has glucose attached to it.
Here are the general interpretations of HbA1c levels:

What are the benefits of keeping HbA1c levels in reasonable limits?
In order to diagnose diabetes, the American Diabetes Association has recommended glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) as a substitute to fasting blood glucose.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a valuable blood test that provides information about a person’s average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. The test measures the percentage of hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells) that has glucose attached to it.
Here are the general interpretations of HbA1c levels:
Keeping HbA1c levels under control offers the favorable outcomes:
- Reduces hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia risk
- Minimizes risk of complications associated with diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy
- Decreases the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke
- Facilitate ulcer healing without increase of mortality in diabetic foot ulcer patients
- Increases adherence to prescribed therapies
- Reduce hospitalizations and visits to emergency rooms, thereby decreasing healthcare expenditures
- Enhances patient satisfaction rate
- Improves quality of life
Role of Genomics in Early and Asymptomatic Diagnosis of Diabetes
Genomic research identifies specific genetic markers, enabling targeted screenings and proactive interventions for individuals at an elevated risk of diabetes.
Genomic testing distinguishes diabetes types (Type 1, Type 2, MODY, gestational), each with unique genetic signatures, guiding healthcare professionals in tailoring precise treatment plans based on genomic insights.
Genomics aids early diagnosis in asymptomatic cases by revealing genetic markers, enabling preventive strategies and lifestyle modifications to mitigate diabetes risk before symptoms manifest.
Unlike basic tests, genomic approaches offers the following benefits:
- Early detection and prevention
- Individualized treatment approaches
- Better familial risk management and clinical course prediction
- Family screening and genetic counseling
- Precision medicine and drug development
How can pharmacogenomics help in optimizing therapy?
The ultimate goal of pharmacogenomics is to recommend the right medicine at the right dose at the right time for the right patient to receive the best treatment outcomes. How is it possible?
Certain genes can influence the process of drug metabolism, drug targets, and drug transporters, leading to a significant impact on drug efficacy and safety. Variations in these genes can result in varied drug responses, encompassing a lack of response, better effectiveness, or maximum susceptibility to adverse reactions which can be analyzed using genomics tests.
The integration of pharmacology and genomics utilizes the analysis of genetic variations in an individual’s DNA to predict their response to specific drugs and adverse reactions. By uncovering these pharmacogenomic associations, doctors can customize diabetes treatment plans to reap the following benefits:
- Increased response to therapy
- Necessity for dose adjustments
- Suggestions on alternative medications
- Minimal adverse events
- Improved quality of life
Here’s an example: The most common forms of MODY are caused by mutations in glucokinase ((GCK-MODY) and hepatic nuclear factor 1 alpha or 4 alpha (HNF1A-MODY and HNF4A-MODY) genes and account for almost 80% of cases of MODY.
MODY is commonly misdiagnosed as type 1 or type 2 diabetes and, as a result, patients are often inappropriately managed with insulin when they can be more effectively managed with oral sulfonylureas.
Making the right diagnosis is critical for effective treatment. This is where, comprehensive monogenic panel along with pharmacogenomics prove to be crucial in treatment optimization. If the patient gets positive result for monogenic panel (HNF1A-MODY) and is already under insulin treatment, he can successfully transition to sulfonylureas (HNF1A-MODY).
Thus, the utilization of pharmacogenomics plays a significant role in optimizing diabetes drug treatments according to the unique DNA makeup of every individual.
References
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2047487319881021
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7843214/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes#:~:text=Overview,hormone%20that%20regulates%20blood%20glucose.
- (https://www.cureus.com/articles/177570-advances-in-the-management-of-diabetes-mellitus-a-focus-on-personalized-medicine#!/)
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6349287/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4933534/